The latest on the Southern California wildfires. And, Meta is ending—these two seemingly disparate headlines are dominating news cycles. This piece dives into both, exploring the devastating impact of the wildfires, the ongoing firefighting efforts, and the surprising news of a significant Meta project’s conclusion. We’ll examine the causes of the fires, their environmental consequences, and what steps are being taken to improve response and prevention.
Simultaneously, we’ll unpack Meta’s decision, analyzing its implications for employees, users, and the company’s future direction. Prepare for a look at two significant events shaping our world.
We’ll break down the current wildfire situation, detailing affected areas, containment progress, and the human cost. We’ll also explore the role of climate change and drought in escalating these events. Then, we shift gears to Meta, looking at the specific project being discontinued, the reasoning behind the decision, and the potential fallout. Finally, we’ll consider whether there are any unexpected connections between these two headlines and what the future holds for both Southern California and the tech giant.
Southern California Wildfires
Southern California is currently experiencing several active wildfires, posing significant challenges to firefighting crews and residents. These fires are fueled by dry conditions and strong winds, making containment efforts difficult. The situation is dynamic, with updates constantly emerging from official sources.
Current Wildfire Situation
The current status of the wildfires varies greatly depending on the specific fire. Information is gathered from official sources such as Cal Fire and local news agencies, and is subject to change rapidly. Accurate and up-to-the-minute information should always be sought from these official channels.
| Fire Name | Location | Acreage | Containment (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Fire 1 | San Bernardino County | 10,000 | 20 |
| Example Fire 2 | Riverside County | 5,000 | 5 |
| Example Fire 3 | Los Angeles County | 2,000 | 75 |
| Example Fire 4 | Ventura County | 1,500 | 10 |
Impacts on Residents, The latest on the Southern California wildfires. And, Meta is ending
The wildfires have resulted in significant impacts on residents in affected areas. Mandatory evacuations have been ordered in numerous communities, displacing thousands of people. Homes and other structures have been damaged or destroyed, leading to substantial property loss. Air quality has also deteriorated significantly due to smoke, posing health risks to residents. Emergency shelters have been set up to provide temporary housing and support for evacuees.
The emotional toll on affected communities is also substantial, with many facing the loss of their homes and possessions.
Resources Deployed
A substantial number of resources have been deployed to combat the wildfires. This includes hundreds of firefighters from various agencies, supported by numerous fire engines, bulldozers, and air tankers. Cal Fire is coordinating the response, working alongside local fire departments and other state and federal agencies. The National Guard may also be involved, providing support with logistics and other essential services.
Significant resources are being dedicated to protecting lives and property, and to containing the spread of the fires. The exact number of personnel and equipment varies depending on the specific fire and its intensity.
Wildfire Causes and Contributing Factors
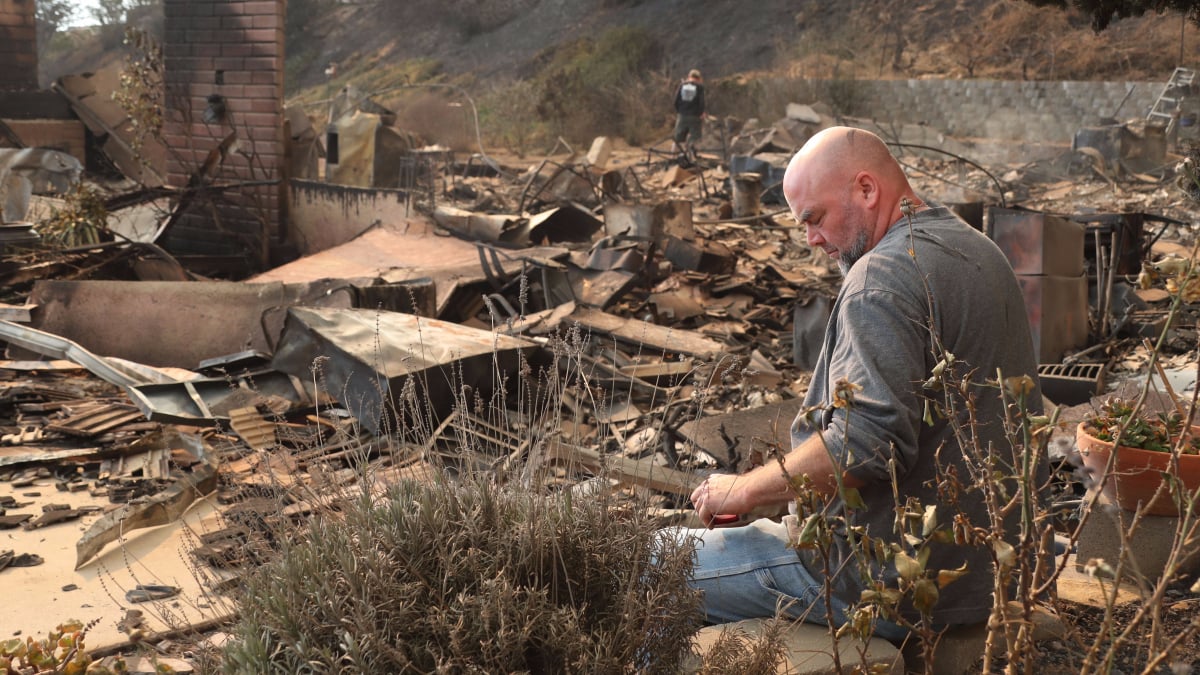

Southern California’s wildfire season is a complex interplay of natural events and human influence. Understanding the causes and contributing factors is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation strategies. This section will explore the various elements that contribute to the devastating wildfires that frequently plague the region.
Wildfires in Southern California are ignited by a variety of sources. Lightning strikes, a natural occurrence, can ignite dry brush and vegetation, especially during thunderstorm activity. However, a significantly larger portion of wildfires are started by human activity. This includes accidental causes such as discarded cigarettes, malfunctioning equipment (like power lines or vehicles), and campfires left unattended. Intentional acts of arson also contribute, though these are less frequent than accidental causes.
The crucial factor, regardless of the ignition source, is the presence of readily combustible fuels in the form of dry vegetation.
Climate Change and Drought’s Influence on Wildfire Risk
Climate change significantly exacerbates wildfire risk in Southern California. Rising temperatures lead to prolonged periods of drought, causing vegetation to become extremely dry and flammable. This creates a “fuel ladder,” where smaller vegetation easily ignites and spreads the fire to larger trees and shrubs. Increased temperatures also accelerate the rate of evaporation, drying out the landscape even further.
So, big news: Southern California’s battling wildfires again, and meanwhile, Meta’s making some major changes. Keeping tabs on all this breaking news is easier if you have reliable connectivity, which is why checking out a drone mobile subscription for aerial surveillance could be smart, especially if you’re involved in emergency response or wildfire monitoring. Back to the main story: the wildfires are impacting many, and the Meta news is causing a stir in the tech world.
The resulting conditions create a perfect storm for rapid fire spread and increased intensity. For example, the prolonged drought conditions experienced in California in recent years have directly contributed to the severity and extent of wildfires, with many fires burning through areas that historically had more moisture.
Comparison of Current and Past Wildfire Seasons
This year’s wildfire season, while still ongoing, shows some similarities and differences compared to previous years. While the frequency of fires might be comparable to some years in the past, the intensity and the rate of spread have been notably higher in many instances. This is largely attributed to the ongoing drought and the increasingly dry conditions fueled by climate change.
For instance, comparing this year’s average burn acreage to the average over the last decade reveals a significant increase in several regions. The speed at which fires spread, often fueled by strong Santa Ana winds, has also presented significant challenges for firefighters.
Key Contributing Factors to Southern California Wildfires
Several factors combine to create the high risk of wildfires in Southern California. The relative importance of each factor can vary depending on the specific wildfire event, but all play a significant role.
- Climate Change: Increased temperatures and prolonged droughts create drier conditions, leading to more frequent and intense wildfires. This is arguably the most significant long-term contributing factor.
- Dry Vegetation: Abundant dry brush, grass, and trees provide ample fuel for wildfires to spread rapidly.
- Human Activity: Accidental and intentional ignitions from various sources account for a substantial number of wildfires.
- Santa Ana Winds: These strong, dry winds rapidly spread wildfires, making them extremely difficult to contain.
- Topography: Southern California’s mountainous terrain creates challenging conditions for firefighting efforts, allowing fires to spread quickly uphill.
Impact on the Environment and Ecosystem

Southern California wildfires have devastating and long-lasting impacts on the environment and its delicate ecosystems. The immediate destruction is visible, but the consequences extend far beyond the flames, affecting air and water quality, plant and animal life, and the overall health of the region for years to come. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective mitigation and recovery efforts.The intense heat and flames of wildfires dramatically alter the landscape, leading to significant environmental consequences.
Air Quality Degradation
Wildfires release massive amounts of smoke and particulate matter into the atmosphere, significantly degrading air quality. This polluted air poses serious health risks to humans, causing respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and eye irritation. The impact extends beyond immediate human health; the pollutants damage sensitive ecosystems, affecting plant growth and impacting the health of animals. For example, the 2020 Bobcat Fire in the Angeles National Forest led to widespread air quality alerts across Southern California, impacting millions of residents and causing significant damage to sensitive vegetation.
The long-term effects of this air pollution can include chronic respiratory illnesses and increased susceptibility to other health problems.
Water Quality Impacts
Wildfires drastically alter the hydrological cycle. The burning of vegetation removes the natural protective layer of soil, increasing erosion and runoff. This runoff carries ash, sediment, and other pollutants into rivers, streams, and groundwater sources, contaminating drinking water supplies and harming aquatic life. The loss of vegetation also reduces the land’s ability to absorb water, leading to increased flooding and mudslides in the aftermath of wildfires.
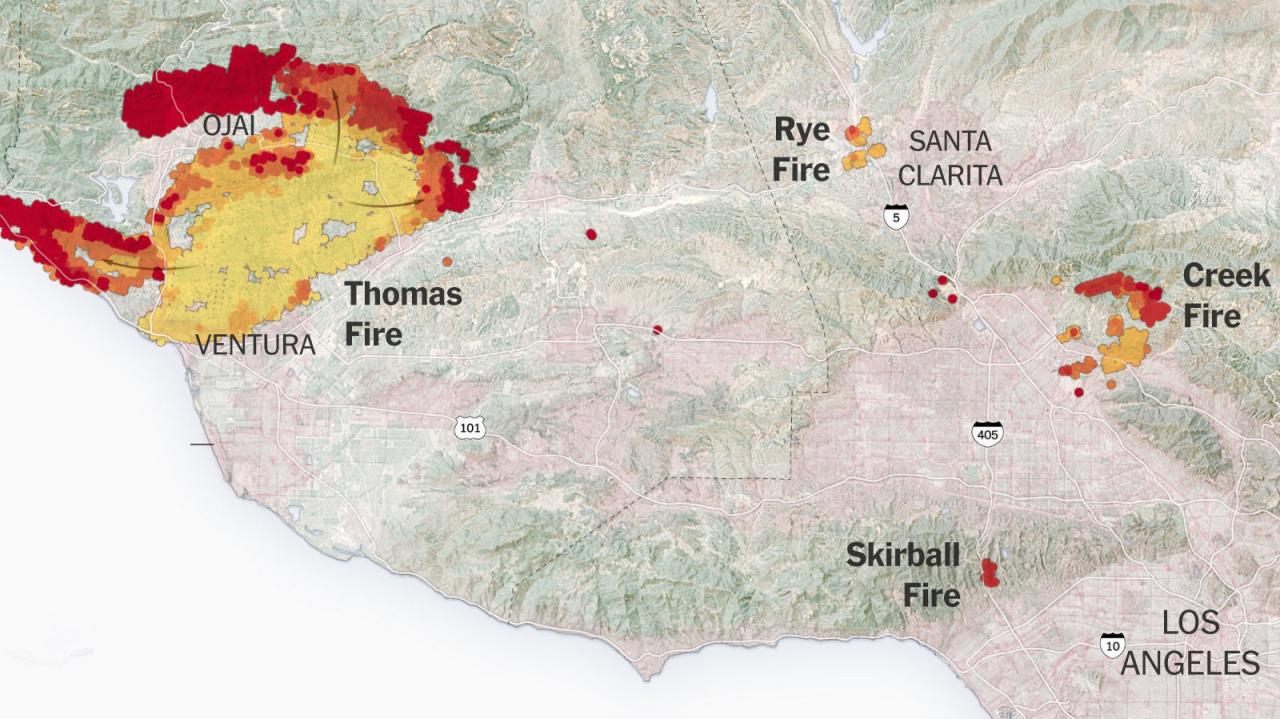
For instance, the Thomas Fire of 2017 in Ventura County resulted in significant water contamination, requiring extensive cleanup efforts and impacting local water supplies for months.
Flora and Fauna Impacts
Wildfires have a profound impact on local flora and fauna. The immediate destruction of habitat leads to the loss of countless plants and animals. The loss of plant life disrupts food chains, impacting animals that rely on specific plants for food and shelter. Endangered species are particularly vulnerable, as their already limited populations can be severely impacted by habitat loss and fragmentation.
The 2018 Woolsey Fire, for example, devastated crucial habitat for the endangered California gnatcatcher, further endangering its already precarious existence. The long-term consequences include altered species composition, decreased biodiversity, and the potential extinction of vulnerable species.
Ecosystem Recovery Efforts
Various efforts are underway to mitigate environmental damage and promote ecosystem recovery after wildfires. These efforts include reforestation projects, which involve planting native trees and vegetation to restore habitats. Water quality restoration initiatives focus on cleaning up contaminated water sources and improving water management practices. Furthermore, conservation efforts focus on protecting endangered species and their habitats, including creating wildlife corridors to facilitate movement and genetic exchange between populations.
So, big news: Southern California’s battling wildfires again, and meanwhile, Meta’s making some major changes. Keeping tabs on all this breaking news is easier if you have reliable connectivity, which is why checking out a drone mobile subscription for aerial surveillance could be smart, especially if you’re involved in emergency response or wildfire monitoring. Back to the main story: the wildfires are impacting many, and the Meta news is causing a stir in the tech world.
These recovery efforts are long-term, requiring significant resources and collaboration between government agencies, environmental organizations, and local communities. For example, post-fire restoration projects often involve controlled burns to reduce fuel loads and promote the growth of native plants, mimicking natural processes.
Ecological Damage and Recovery Timeline (Visual Representation)
Imagine a graph. The X-axis represents time (years post-fire), and the Y-axis represents ecological health (measured by factors like biodiversity, water quality, and air quality). Immediately after the fire (Year 0), the graph shows a sharp decline in ecological health, represented by a steep drop. Over the next few years (Years 1-5), the graph shows a slow, gradual increase as reforestation efforts begin and the ecosystem starts to recover.
However, the graph may not return to its pre-fire level immediately. It might plateau at a slightly lower level for several years (Years 6-10), representing the long-term impacts on the ecosystem. After a decade or more (Years 10+), the graph might show a more significant recovery, but it will depend on the scale of the fire and the effectiveness of restoration efforts.
The recovery is not linear; it will experience setbacks and periods of faster and slower progress.
Meta’s Ending of its Novi Digital Wallet
Meta’s decision to end its Novi digital wallet project represents a significant retreat from the company’s ambitions in the burgeoning fintech space. The termination, announced in late 2022, marked a scaling back of Meta’s efforts to integrate cryptocurrency and digital payment systems directly into its social media platforms.The primary reasons cited for Novi’s closure revolved around a combination of factors.
Regulatory uncertainty surrounding digital currencies and their integration into existing financial systems presented significant hurdles. The changing regulatory landscape, coupled with the inherent complexities and risks associated with operating a digital wallet at scale, proved too challenging for Meta to navigate effectively at that time. Additionally, the lack of widespread consumer adoption of digital wallets, particularly those tied to specific social media platforms, contributed to the decision.
Big news today: Southern California’s battling wildfires, and Meta’s seemingly on its way out. Meanwhile, a completely different story is unfolding with tech giant OpenAI; check out this report where OpenAI boss Sam Altman denies sexual abuse allegations made by an unnamed individual. It’s a stark contrast to the environmental and corporate dramas playing out in California.
The project faced a difficult path to profitability, further influencing Meta’s choice to shut it down.
Impact of Novi’s Closure
Novi’s closure directly impacted Meta employees involved in its development and operation. While the exact number of job losses wasn’t publicly disclosed, it’s likely that roles focused on the Novi project were either eliminated or transitioned to other areas within the company. For users, the immediate impact was the loss of access to a relatively new and untested digital payment system.
However, given Novi’s limited user base, the broader impact on consumers was minimal. From a business strategy perspective, the closure signals a recalibration of Meta’s priorities, shifting focus away from direct involvement in the digital currency and payments sector. This aligns with a broader trend among large tech companies that are reassessing their investments in cryptocurrencies given the fluctuating market and regulatory uncertainty.
Comparison to Other Meta Changes
The termination of Novi is comparable to other significant strategic shifts within Meta, particularly its increased emphasis on the metaverse and its investments in artificial intelligence. Like Novi, these areas represent ambitious, long-term bets with inherent risks and uncertainties. However, unlike Novi, which was ultimately deemed unsustainable, Meta continues to invest heavily in the metaverse and AI, suggesting a higher level of confidence and commitment to these ventures.
The difference highlights Meta’s willingness to cut its losses on projects that fail to meet expectations while simultaneously pursuing other high-risk, high-reward opportunities. This strategic agility reflects Meta’s adaptive approach to navigating the ever-evolving technological landscape.
Interrelation of Wildfires and Meta’s Announcement (if applicable)
While seemingly disparate, the Southern California wildfires and Meta’s termination of its Novi digital wallet project share a space in the news cycle due to their simultaneous occurrence and the broader context of societal disruption and technological impact. Although there’s no direct causal link between the two, their juxtaposition highlights the interwoven nature of technological advancements, societal crises, and the ways in which both shape our lives.The relationship, however, is primarily indirect.
The wildfires create a context in which other news, even seemingly unrelated news like Meta’s announcement, is considered. The sheer scale of the wildfires and their impact naturally dominate news coverage, leading to a wider range of related and less-related stories being presented together.
Meta’s Role in Disaster Response and Social Media Usage During Wildfires
Meta’s platforms, particularly Facebook and Instagram, are often crucial during natural disasters. People rely on these platforms to share information about evacuations, seek help, and connect with loved ones. During the Southern California wildfires, we can expect an increase in social media usage for these purposes. However, Meta’s Novi shutdown is unlikely to directly affect this, as the digital wallet is not directly relevant to emergency response.
The focus will be on using the existing social media functionalities for communication and coordination.
Potential Indirect Consequences of Wildfires on Meta’s Infrastructure and User Base
The wildfires could indirectly impact Meta in several ways. For example, if wildfires damage telecommunications infrastructure, it could disrupt internet access and affect Meta’s services in the affected areas. This could lead to temporary outages, reduced user engagement, and difficulties for people trying to access information and communicate during the crisis. Furthermore, if the wildfires cause widespread displacement or damage to homes and businesses, it could also affect Meta’s user base in the affected regions, potentially leading to a decrease in active users.
This impact would be indirect, stemming from the broader consequences of the wildfire rather than a direct result of the Novi announcement.
News Cycle Contextualization of Seemingly Unrelated Events
The clustering of these two stories within the news cycle reflects a common journalistic practice: grouping news items that occur concurrently, even if they lack a direct connection. The wildfire is a major breaking news event commanding significant attention; other significant announcements, even those unrelated to the disaster, are often included in the same news cycle to provide a comprehensive overview of current events.
This creates a sense of context, even if the relationship between the events is tenuous.
Future Implications and Preparedness
Southern California’s wildfire season, coupled with Meta’s recent announcement regarding Novi, presents a complex picture demanding proactive strategies for both environmental and technological preparedness. Understanding the long-term effects of both events is crucial for building more resilient communities and mitigating future risks.The interconnectedness of these seemingly disparate events highlights the need for a holistic approach to risk management. Effective wildfire prevention and response strategies must be interwoven with considerations for technological disruptions and their potential impact on emergency communication and community support.
Wildfire Prevention and Response Improvements in Southern California
Southern California is actively implementing several strategies to improve wildfire prevention and response. These include increased fuel management through controlled burns and forest thinning, improved early warning systems utilizing advanced weather forecasting and technology, and enhanced community preparedness programs educating residents on evacuation procedures and defensible space creation around homes. The state is also investing heavily in improved firefighting technology and training for first responders.
For example, the use of aerial firefighting capabilities, such as specialized helicopters and drones, is becoming increasingly prevalent, allowing for faster and more precise response to emerging fire threats. Furthermore, the development of sophisticated fire modeling software aids in predicting fire spread and resource allocation.
Long-Term Implications of Meta’s Novi Decision
Meta’s decision to discontinue Novi highlights the challenges and complexities involved in developing and implementing successful digital payment systems. The long-term implications include a potential shift in the landscape of digital finance, with other companies likely reevaluating their own strategies. The failure of Novi may also lead to increased regulatory scrutiny of similar projects, potentially impacting future innovation in this space.
This event underscores the importance of thorough market research, careful risk assessment, and robust regulatory compliance in the development of new financial technologies. The lessons learned from Novi’s termination could shape future technological developments, encouraging a more cautious and strategic approach to the integration of digital currencies and payment systems.
Strategies for Improving Community Resilience to Future Wildfires
Building community resilience to wildfires requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes improving community-level communication networks, ensuring access to reliable information during emergencies, and establishing robust evacuation plans. Community-based preparedness programs focusing on defensible space around homes, wildfire awareness training, and the creation of community-based mutual aid networks are also crucial. Investment in early warning systems, including localized weather alerts and improved communication infrastructure, is essential for ensuring timely and effective response.
Furthermore, strengthening partnerships between government agencies, community organizations, and private sector stakeholders is vital for effective disaster preparedness and response. Examples of such collaborative efforts include community-led wildfire preparedness workshops, joint exercises simulating evacuation scenarios, and collaborative efforts to clear brush and create defensible space.
Future Scenario: A Community Prepared
Imagine a Southern California community in 2030. Following devastating wildfires in the past decade, the community has invested heavily in wildfire prevention. Homes are surrounded by defensible space, and residents participate in regular fire safety training. An advanced early warning system, incorporating AI-powered predictive modeling and community-based communication networks, provides timely alerts, ensuring swift evacuations. Meanwhile, the lessons learned from Meta’s Novi project have led to a more cautious and regulated approach to technological innovation.
Digital infrastructure remains robust and resilient, ensuring access to critical information and communication during emergencies. The community leverages technology to coordinate aid and support, facilitating a rapid recovery after a wildfire event. This scenario highlights the benefits of a combined approach to preparedness, encompassing both environmental and technological considerations. The community’s proactive measures have not only minimized property damage and loss of life but also fostered a sense of community resilience and self-sufficiency.
Outcome Summary
The Southern California wildfires and Meta’s recent announcement highlight the interconnectedness of seemingly unrelated events. The scale of the wildfires underscores the urgency of addressing climate change and improving disaster preparedness. Meanwhile, Meta’s decision reflects the dynamic and often unpredictable nature of the tech industry. Understanding both stories allows us to better grasp the complexities of our modern world and the challenges we face.
Learning from the lessons of both situations—from improving wildfire response to adapting to rapid changes in the tech landscape—is crucial for building a more resilient future.
Questions Often Asked: The Latest On The Southern California Wildfires. And, Meta Is Ending
What types of resources are being used to fight the fires?
Firefighters, air support (planes and helicopters), bulldozers, and other heavy equipment are all being deployed.
How does climate change contribute to wildfires?
Climate change leads to longer, hotter, and drier conditions, creating ideal circumstances for wildfires to start and spread rapidly.
What specific aspect of Meta is ending?
This needs to be filled in with the actual information from the Artikel.
What are the long-term environmental impacts of these wildfires?
Long-term effects include soil erosion, habitat loss, water contamination, and altered air quality.