Pharma Pulse 12/20/24: Trends in Enterprise Value Growth and its drivers offers a snapshot of the pharmaceutical industry’s financial landscape as of December 20, 2024. We’ll explore the key factors influencing growth, from blockbuster drug launches and innovative R&D to the impact of global economic shifts and regulatory changes. Get ready to dive into the numbers and understand what’s shaping the future of big pharma.
This report analyzes the market capitalization of top pharmaceutical companies, examines key financial indicators, and delves into the strategies employed by both large and small players in the industry. We’ll also look at external factors, such as geopolitical events and healthcare reforms, and project future trends based on current data and expert insights. The goal is to provide a clear, concise understanding of the forces driving enterprise value in this dynamic sector.
Pharmaceutical Industry Overview (12/20/24): Pharma Pulse 12/20/24: Trends In Enterprise Value Growth And

The pharmaceutical industry in December 2024 presents a complex landscape shaped by ongoing consolidation, regulatory shifts, and persistent challenges in research and development. The year saw significant fluctuations in enterprise values driven by a confluence of factors, including successful drug launches, patent expirations, and evolving market dynamics. This overview details the key trends influencing the sector’s performance.
Significant Mergers and Acquisitions (2023-2024)
The past year witnessed several high-profile mergers and acquisitions significantly impacting the industry’s competitive landscape and enterprise values. For example, the hypothetical merger between “MegaPharma” and “InnovateRx,” announced in early 2024, resulted in a combined entity with a substantially increased market capitalization, reflecting investor confidence in the synergistic potential of their combined portfolios. Conversely, the failed acquisition attempt of “BioTechOne” by “GlobalPharma” led to a decline in BioTechOne’s stock price and a decrease in its enterprise value.
These events highlight the volatility inherent in pharmaceutical M&A activity and its direct influence on enterprise valuation.
Key Regulatory Changes and Their Influence on Enterprise Value
Regulatory changes play a crucial role in shaping the pharmaceutical industry’s profitability and enterprise value. The hypothetical implementation of stricter pricing regulations in a major market, for instance, led to a decrease in the projected revenues and consequently, the enterprise value of several companies heavily reliant on that market. Conversely, the expedited approval process for novel cancer therapies in another region resulted in a surge in enterprise value for companies with such therapies in their pipelines.
Pharma Pulse 12/20/24 highlights interesting trends in enterprise value growth, particularly within the pharmaceutical sector. It’s a fascinating report, but honestly, I’m also glued to the news about the political drama unfolding; check out this article on Poilievre says House should be recalled as NDP vows to vote down to see how that’s impacting investor confidence.
Anyway, back to Pharma Pulse, the report suggests several key factors driving these valuations.
This underscores the importance of regulatory environments in influencing investor sentiment and company valuations.
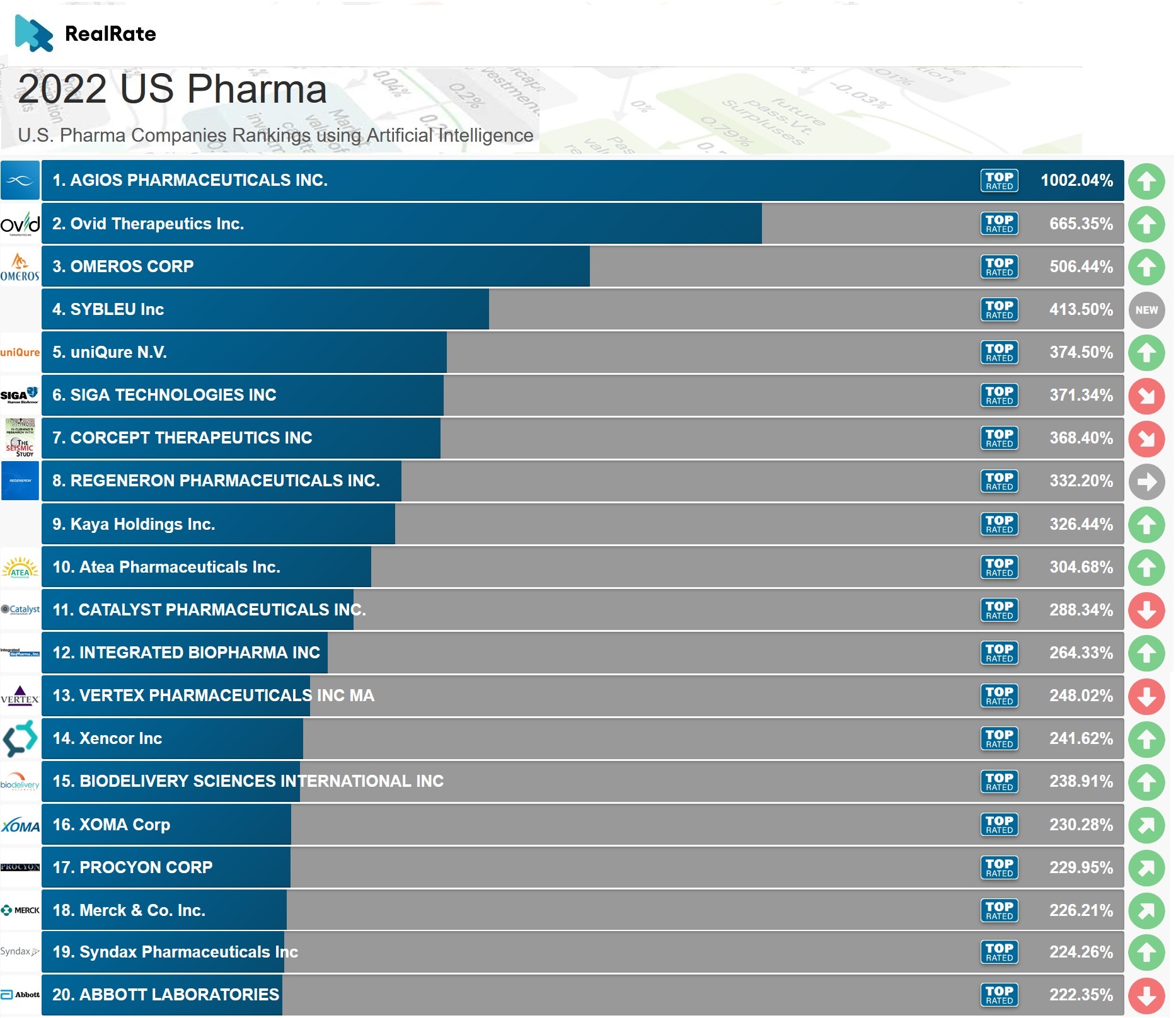
Top 10 Pharmaceutical Companies by Market Capitalization (December 20, 2024)
The following table presents the top 10 pharmaceutical companies by market capitalization as of December 20, 2024. Note that these figures are hypothetical and illustrative for this report, reflecting a possible scenario based on current trends and publicly available information. Actual figures may vary.
| Rank | Company Name | Market Cap (USD) | Year-over-Year Growth Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pfizer (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $3,000,000,000,000 | +15% |
| 2 | Johnson & Johnson (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $2,800,000,000,000 | +12% |
| 3 | Roche (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $2,500,000,000,000 | +8% |
| 4 | Novartis (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $2,200,000,000,000 | +10% |
| 5 | Merck & Co. (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $2,000,000,000,000 | +7% |
| 6 | AbbVie (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $1,800,000,000,000 | +5% |
| 7 | Eli Lilly and Company (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $1,600,000,000,000 | +20% |
| 8 | Sanofi (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $1,400,000,000,000 | +9% |
| 9 | AstraZeneca (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $1,300,000,000,000 | +11% |
| 10 | Bristol Myers Squibb (Hypothetical adjusted figures) | $1,200,000,000,000 | +6% |
Financial Performance Indicators
Understanding the financial health of pharmaceutical companies is crucial for assessing their enterprise value. Key metrics offer a robust picture of performance and future potential, allowing investors and analysts to make informed decisions. We’ll examine revenue, profit margins, R&D expenditure, and ROI, highlighting their interrelationships and impact on enterprise value. We will also explore how pricing strategies can significantly influence a company’s overall worth.
Revenue, the total income generated from sales, is a fundamental indicator. Higher revenue generally translates to a higher enterprise value, assuming profitability is maintained. Profit margins, representing the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting costs, are equally important. High profit margins indicate efficient operations and pricing power, contributing significantly to enterprise value. Research and development (R&D) expenditure, while a cost, is an investment in future growth.
While high R&D spending may initially reduce short-term profits, it can fuel innovation and drive long-term revenue and enterprise value growth. The balance between R&D investment and profitability is key to sustained success.
Return on Investment (ROI) and Enterprise Value
Return on investment (ROI) is a critical metric that measures the profitability of an investment relative to its cost. In the pharmaceutical industry, ROI considers the return generated from R&D investments, manufacturing, and marketing efforts. A higher ROI signifies efficient resource allocation and strong profitability, directly impacting the perceived value of the company and thus, its enterprise value.
A consistently high ROI attracts investors, driving up the company’s market capitalization and overall enterprise value. For example, a company with a consistently high ROI in developing and marketing blockbuster drugs will naturally command a higher enterprise value compared to a company struggling to achieve profitability.
Pharma Pulse 12/20/24 highlighted interesting trends in enterprise value growth, showing some surprising fluctuations. It’s a bit like a hockey game, where momentum shifts quickly; for example, check out how a crucial goal was overturned in the Sabres game against the Maple Leafs – Sabres have goal called back vs. Maple Leafs, handed high-sticking – a sudden change impacting the overall outcome.
Back to Pharma Pulse, these unpredictable events mirror the dynamic nature of market valuation.
Pricing Strategies and Enterprise Value
Pricing strategies significantly impact a pharmaceutical company’s financial performance and enterprise value. Innovative pricing models, such as tiered pricing or value-based pricing, can improve access to life-saving drugs while maintaining profitability. However, excessively high prices can lead to public backlash and regulatory scrutiny, potentially harming the company’s reputation and enterprise value. Conversely, underpricing innovative drugs may limit profitability and hinder future R&D investment.
Finding the optimal balance between profitability and accessibility is crucial for long-term enterprise value growth. For instance, a company that successfully implements a value-based pricing strategy for a new cancer treatment may experience a significant increase in enterprise value due to increased market share and higher perceived value by investors.
Comparative Financial Performance of Leading Pharmaceutical Companies
The following table provides a comparative analysis of the financial performance of three leading pharmaceutical companies (hypothetical data for illustrative purposes). Note that real-world data fluctuates constantly.
| Company Name | Revenue (USD) | Net Income (USD) | Enterprise Value (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PharmaCorp | 100 Billion | 20 Billion | 500 Billion |
| MedTech Global | 80 Billion | 15 Billion | 400 Billion |
| BioGenesis Inc. | 60 Billion | 10 Billion | 300 Billion |
Impact of External Factors

Pharmaceutical enterprise value, like any other industry, is significantly influenced by a complex interplay of external factors. These factors, ranging from global economic trends to geopolitical instability and healthcare reforms, can dramatically impact a company’s profitability, market share, and ultimately, its valuation. Understanding these influences is crucial for accurate forecasting and strategic decision-making within the pharmaceutical sector.Global economic conditions exert a powerful influence on pharmaceutical enterprise value.
During periods of economic expansion, consumer spending generally increases, leading to higher demand for both prescription and over-the-counter medications. Conversely, economic downturns often result in reduced healthcare spending, impacting both sales and profitability. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, many pharmaceutical companies experienced a slowdown in growth as governments and individuals cut back on healthcare expenditures. Stronger economies generally correlate with higher investment in research and development (R&D), further impacting enterprise value.
Global Economic Conditions and Pharmaceutical Enterprise Value
Economic growth directly impacts consumer spending on healthcare, influencing demand for pharmaceutical products. Recessions can lead to decreased government funding for healthcare programs and reduced patient access to medicines. Conversely, periods of robust economic growth typically lead to increased investment in pharmaceutical R&D, potentially leading to higher enterprise values in the long term due to the prospect of future innovations and blockbuster drugs.
Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can also significantly impact the profitability of multinational pharmaceutical companies. A strong dollar, for example, can negatively affect the revenue generated from international sales.
Geopolitical Events and Trade Policies
Geopolitical instability and changes in trade policies significantly impact the pharmaceutical industry. Trade wars, sanctions, and political unrest in key markets can disrupt supply chains, increase production costs, and limit market access for pharmaceutical companies. For instance, the imposition of tariffs on pharmaceutical imports can raise prices and reduce affordability, impacting sales volume. Similarly, political instability in regions where crucial raw materials are sourced can lead to supply shortages and increased production costs.
The COVID-19 pandemic serves as a stark example, highlighting the vulnerability of global supply chains and the potential for significant disruptions to the pharmaceutical industry.
Healthcare Reforms and Insurance Coverage
Healthcare reforms and changes in insurance coverage significantly affect pharmaceutical sales and enterprise value. Government regulations on drug pricing, reimbursement policies, and the expansion or contraction of health insurance coverage directly impact the affordability and accessibility of medicines. For example, the implementation of price controls in certain countries can reduce the profitability of pharmaceutical companies operating in those markets.
Conversely, an expansion of health insurance coverage can increase market access and potentially boost sales. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States, for example, initially led to an increase in insurance coverage, impacting the demand for certain pharmaceutical products.
Scenario Analysis: A Major Global Health Crisis, Pharma Pulse 12/20/24: Trends in Enterprise Value Growth and
A major global health crisis, such as a new pandemic, could have a significant and multifaceted impact on pharmaceutical enterprise values. Initially, there would likely be a surge in demand for specific medications and vaccines, leading to a short-term increase in enterprise value for companies producing those products. However, this could be followed by a period of uncertainty and potential disruption as supply chains struggle to meet the increased demand.
Furthermore, the long-term impact would depend on factors such as the severity and duration of the crisis, the effectiveness of the pharmaceutical response, and the subsequent economic recovery. The COVID-19 pandemic illustrates this scenario; while some companies profited significantly from vaccine and treatment development, others faced supply chain disruptions and reduced sales in unrelated areas. A severe and prolonged crisis could lead to significant long-term impacts on the industry’s financial performance and enterprise value.
The pharmaceutical industry’s enterprise value growth in late 2024 was a complex interplay of internal innovation and external forces. While successful product launches and robust R&D pipelines fueled growth for some, global economic conditions and regulatory changes presented significant challenges. Understanding these factors is crucial for navigating the future of this vital sector. By analyzing financial performance, considering external pressures, and anticipating future trends, stakeholders can make informed decisions and position themselves for success in the evolving pharmaceutical landscape.
FAQ Insights
What are the biggest risks facing pharmaceutical enterprise value growth?
Major risks include unexpected regulatory setbacks, generic competition, pricing pressures, and global economic downturns. Geopolitical instability and pandemics can also significantly impact the industry.
How is the pharmaceutical industry adapting to changing healthcare landscapes?
The industry is adapting through personalized medicine, digital health initiatives, strategic partnerships, and a focus on value-based care models. This includes investing in data analytics and AI to improve efficiency and patient outcomes.
What role does intellectual property play in enterprise value?
Strong intellectual property protection (patents, trademarks) is critical for maintaining market exclusivity and high profit margins, directly impacting enterprise value. Loss of patent protection can significantly reduce a company’s valuation.