Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it? This respiratory virus, related to RSV and influenza, is causing concern as cases surge. Understanding its transmission, symptoms, and treatment is crucial for protecting children. We’ll explore HMPV’s characteristics, the factors driving its spread in China, and steps to mitigate its impact.
This article will delve into the specifics of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), explaining its genetic makeup, transmission methods, and the symptoms it causes in children. We’ll compare it to other common respiratory viruses and discuss the current situation in China, including potential contributing factors like reduced immunity post-COVID-19 restrictions. Finally, we’ll explore preventative measures and public health strategies to combat this rising threat.
What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
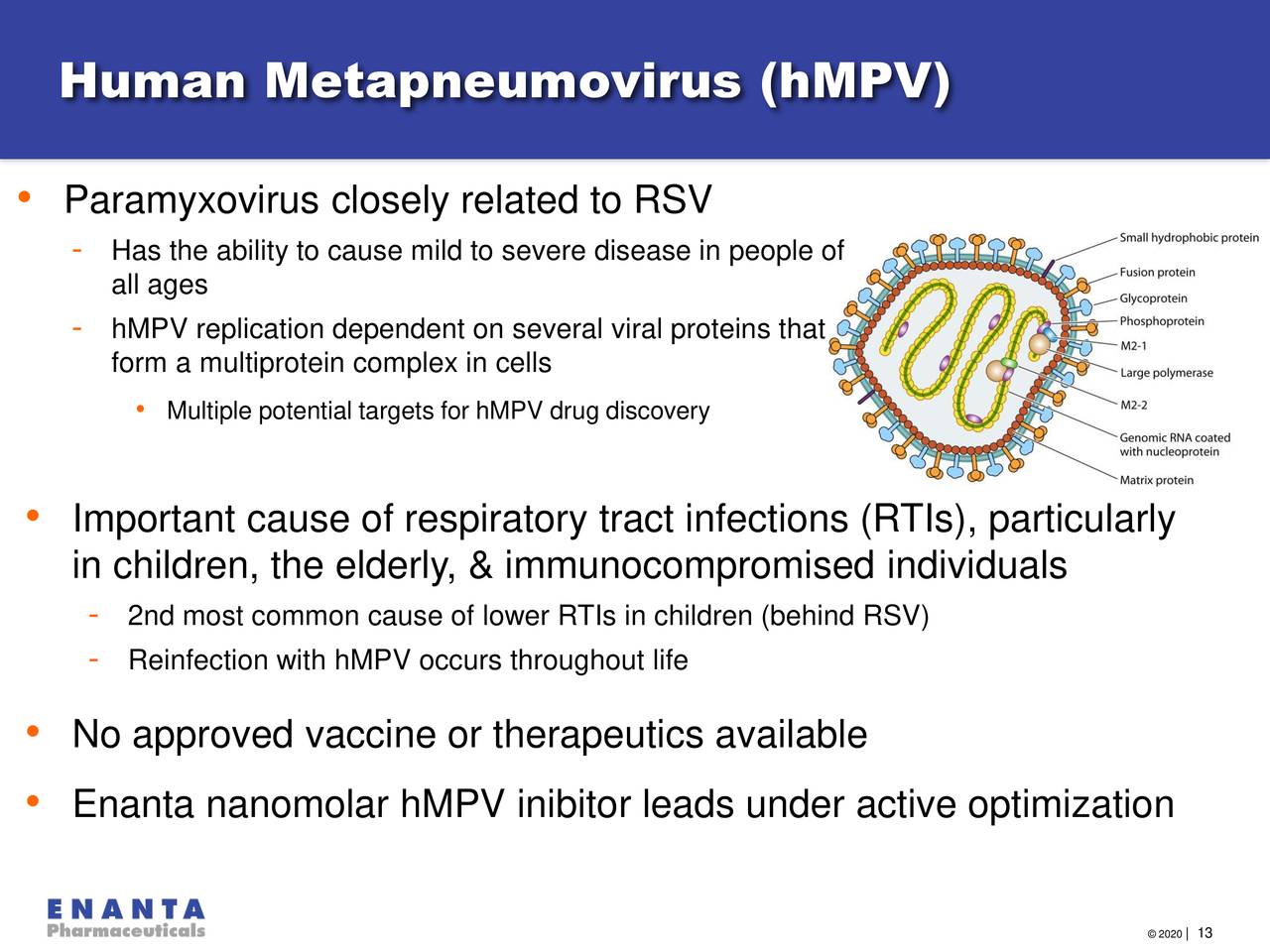
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common respiratory virus that can cause mild to severe respiratory illnesses, particularly in young children and older adults. It’s a member of the Paramyxoviridae family, closely related to other respiratory viruses like RSV and influenza. Understanding its structure, genetic makeup, and how it compares to other viruses helps in prevention and treatment strategies.
HMPV Structure and Genetic Makeup
HMPV, like other paramyxoviruses, is an enveloped virus with a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome. The virus particle is roughly spherical, with a lipid envelope studded with glycoproteins, notably the fusion (F) and attachment (G) proteins. These glycoproteins are crucial for the virus to attach to and enter host cells. The RNA genome encodes several proteins essential for viral replication and assembly.
Genetic variations within these genes account for the different genotypes and subtypes of HMPV.
HMPV Genotypes and Subtypes
HMPV is classified into two major genotypes, A and B. Each genotype is further subdivided into several subtypes. These genetic differences affect the virus’s ability to infect and cause disease, although the clinical manifestations are often similar across subtypes. The exact prevalence of each genotype and subtype can vary geographically and temporally. Research is ongoing to understand the full implications of these genetic variations.
Comparison of HMPV with RSV and Influenza, Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it?
HMPV shares similarities with other respiratory viruses, particularly respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza viruses, in terms of the symptoms they cause and their transmission routes. However, there are also key differences. All three viruses primarily infect the respiratory tract, causing varying degrees of illness. Understanding these differences is important for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Key Differences Between HMPV, RSV, and Influenza
| Virus Name | Symptoms | Transmission | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMPV | Symptoms range from mild cold-like symptoms (cough, runny nose, fever) to more severe lower respiratory tract infections (bronchiolitis, pneumonia), especially in infants and young children. | Spread through respiratory droplets produced during coughing or sneezing. Close contact with infected individuals is the primary mode of transmission. | Severity varies; generally milder than RSV in older children and adults, but can be severe in infants and those with underlying health conditions. |
| RSV | Similar to HMPV, symptoms can range from mild upper respiratory illness to severe lower respiratory tract infections (bronchiolitis, pneumonia), particularly in infants and young children. | Spread through respiratory droplets and direct contact. | Can be more severe than HMPV, especially in infants and those with compromised immune systems. |
| Influenza | Symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. Can range from mild to severe illness, including pneumonia and other complications. | Spread through respiratory droplets and airborne transmission. | Severity varies widely; some strains can cause more severe illness and complications, especially in high-risk groups (elderly, young children, immunocompromised individuals). |
Transmission and Spread of HMPV: Viral Disease HMPV Is On The Rise Among Kids In China — What Is It?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) spreads easily from person to person, primarily through respiratory droplets produced when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. These droplets can then be inhaled by others in close proximity, leading to infection. Understanding how HMPV transmits is crucial for preventing its spread, especially in vulnerable populations like young children.HMPV transmission is influenced by several key factors.
Close contact facilitates the spread of respiratory droplets, making crowded environments like schools and daycare centers high-risk areas. Population density plays a significant role; higher density increases the likelihood of encounters and transmission. Seasonality also impacts HMPV spread, with outbreaks typically peaking during the colder months, mirroring other respiratory viruses. This is likely due to increased time spent indoors, where transmission is more efficient.
Finally, the presence of asymptomatic carriers, individuals infected with HMPV but showing no symptoms, contributes significantly to the virus’s silent spread. These individuals can unknowingly transmit the virus to others.
Primary Modes of HMPV Transmission
HMPV is transmitted primarily through direct contact with respiratory secretions from an infected person. This can occur through direct contact with the infected person’s mouth or nose, or indirectly through contact with contaminated surfaces. The virus can survive on surfaces for a limited time, allowing for indirect transmission.
Factors Influencing HMPV Spread
Several factors contribute to the spread of HMPV. High population density, especially in settings with close contact like schools or daycare centers, increases the probability of transmission. Seasonality is another crucial factor, with colder months typically seeing a rise in cases due to increased indoor gatherings and reduced ventilation. The presence of asymptomatic carriers, who may unknowingly spread the virus, also significantly contributes to the overall spread of HMPV.
For instance, a child attending daycare might spread the virus to other children and even adults without exhibiting any symptoms themselves. This highlights the importance of preventative measures even when symptoms are absent.
The Role of Asymptomatic Carriers in HMPV Transmission
Asymptomatic individuals, those infected with HMPV but exhibiting no symptoms, play a substantial role in transmission. They can unknowingly spread the virus through respiratory droplets produced during normal breathing, talking, or sneezing. Because they don’t experience symptoms, they are less likely to take precautions like isolating themselves, thereby increasing the risk of spreading the virus to others. This silent transmission makes controlling outbreaks more challenging.
Imagine a seemingly healthy child attending school and unknowingly infecting several classmates and teachers.
A Flowchart Illustrating Person-to-Person HMPV Transmission
The following describes a flowchart illustrating the steps of HMPV transmission:
1. Infected Person
An individual infected with HMPV coughs or sneezes, releasing respiratory droplets containing the virus.
2. Droplet Dispersion
These droplets containing the virus travel through the air.
3. Inhalation/Contact
A susceptible individual inhales these droplets or touches a contaminated surface and then touches their eyes, nose, or mouth.
4. Virus Entry
The virus enters the susceptible individual’s respiratory system.
5. Infection
The virus replicates, leading to infection and potential symptom development.
6. Transmission
The newly infected individual can then transmit the virus to others, continuing the cycle.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations of HMPV in Children
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infection in children presents a wide range of symptoms, varying in severity depending on the child’s age and overall health. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and appropriate management. While some children experience only mild cold-like symptoms, others can develop more severe respiratory illnesses requiring hospitalization.HMPV symptoms often mimic those of other common respiratory viruses, making accurate diagnosis challenging without laboratory testing.
The severity and specific symptoms can differ significantly between infants, toddlers, and older children. This variation highlights the importance of careful observation and prompt medical attention if symptoms worsen.
Age-Specific Symptom Variations
Younger children, particularly infants, are more likely to experience lower respiratory tract involvement, such as bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lungs) and pneumonia (lung infection). They may present with difficulty breathing, wheezing, and rapid breathing. Older children, on the other hand, tend to exhibit milder upper respiratory tract symptoms, similar to a common cold, including runny nose, cough, and fever.
Infants may also experience poor feeding, lethargy, and dehydration. These symptoms can be more pronounced in premature infants or those with underlying health conditions.
Worried about the HMPV virus surge impacting kids in China? It’s a serious respiratory illness, and understanding its spread is crucial. If you’re interested in a career helping those affected, consider looking into accredited surgical tech programs near me with clinical rotations to learn more about patient care. Ultimately, combating viral outbreaks like this requires skilled medical professionals, so exploring your options is a great first step.
Potential Complications of HMPV Infection
Severe HMPV infections can lead to various complications, especially in high-risk groups. These complications can include pneumonia, bronchiolitis, croup (inflammation of the larynx and trachea), and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a serious condition characterized by fluid buildup in the lungs. In rare cases, HMPV infection can lead to more severe complications like respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, or even death, particularly in infants with pre-existing conditions like heart or lung disease.
Secondary bacterial infections can also occur, further complicating the illness.
Typical Progression of HMPV Symptoms
The following is a general guideline for the typical progression of HMPV symptoms. It’s important to note that individual experiences can vary significantly.
- Initial Stage (Days 1-3): The illness usually begins with mild symptoms like a runny nose, cough, and low-grade fever. Some children may experience mild sore throat or sneezing.
- Intermediate Stage (Days 4-7): Symptoms may worsen, with a more persistent cough, increased nasal congestion, and potentially higher fever. Some children may develop wheezing or difficulty breathing.
- Resolution Stage (Days 8-14): Symptoms gradually improve, with the cough often persisting for a longer period than other symptoms. Fever typically subsides.
Diagnosis and Treatment of HMPV
Diagnosing and treating Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) infection involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Treatment focuses primarily on supportive care, although antiviral medications may be considered in severe cases. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effective management of HMPV outbreaks, particularly in vulnerable populations like young children.
Diagnostic Methods for HMPV
HMPV is diagnosed primarily through laboratory testing, as symptoms can overlap with other respiratory viruses. Several methods exist, each with varying levels of sensitivity and specificity. Rapid diagnostic tests offer quick results, while more sensitive molecular tests are used for confirmation or in cases where the initial test is inconclusive. Accurate diagnosis is essential to guide appropriate treatment and infection control measures.
Treatment Approaches for HMPV
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for HMPV. The mainstay of treatment is supportive care, which focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. This includes adequate hydration, rest, and management of fever and other symptoms as needed. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide respiratory support, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
Antiviral Medications for Severe HMPV Infections
While no specific antiviral drug targets HMPV, in severe cases, clinicians may consider off-label use of antiviral medications, such as ribavirin, based on the severity of the illness and the patient’s clinical response. However, the effectiveness of these medications in treating HMPV is still under investigation, and their use is generally reserved for severe cases where supportive care alone is insufficient.
The decision to use antiviral medications should be made on a case-by-case basis in consultation with infectious disease specialists.
Comparison of Diagnostic Tests for HMPV
The choice of diagnostic test depends on factors such as the availability of resources, the urgency of results, and the clinical setting. Below is a comparison of common diagnostic methods:
| Test | Method | Sensitivity | Specificity | Turnaround Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Fluorescent Antibody (DFA) | Microscopic detection of viral antigens in respiratory specimens | Moderate (60-80%) | Good (80-90%) | Rapid (within hours) |
| Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | Detection of viral antigens or antibodies in respiratory specimens | Moderate to Good (70-90%) | Good (80-90%) | 1-2 days |
| Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) | Detection of viral RNA in respiratory specimens | High (90-95%) | Excellent (95-99%) | 1-2 days |
The Current Situation in China
The recent surge in Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) cases among children in China is a significant public health concern. Several factors likely contribute to this increase, highlighting the complex interplay between viral dynamics, public health measures, and population immunity. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective prevention and mitigation strategies.The rise in HMPV cases in China appears linked to a confluence of events.
Reduced exposure to common respiratory viruses during the stringent COVID-19 lockdowns likely led to a decrease in population immunity, making children more susceptible to HMPV infection. This phenomenon, known as “immune debt,” has been observed globally following periods of reduced social interaction and infection. Furthermore, the relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions may have increased opportunities for viral transmission, facilitating the spread of HMPV among children.
Other contributing factors could include seasonal variations in HMPV circulation, changes in viral strains, and possibly underlying health conditions in some children. Comparing this current situation with previous HMPV outbreaks requires detailed epidemiological data, but it is plausible that the scale and intensity of the current surge are amplified by the factors mentioned above.
Impact of Reduced Immunity Following COVID-19 Restrictions
The COVID-19 pandemic and the associated lockdowns significantly altered the typical patterns of respiratory virus circulation. Children experienced reduced exposure to various viruses, including HMPV, resulting in a decline in their natural immunity. This “immune debt” made them more vulnerable to infections upon the relaxation of restrictions, leading to a potentially larger and more severe HMPV outbreak than might have otherwise occurred.
The lack of widespread exposure to other respiratory viruses also means that cross-immunity – where exposure to one virus offers some protection against another – may have been reduced, further contributing to the vulnerability of children to HMPV. For example, some studies suggest that prior infection with other respiratory viruses can provide partial protection against HMPV. The absence of this cross-immunity during the pandemic likely amplified the impact of HMPV’s resurgence.
Worried about the HMPV virus surge in China impacting kids? It’s a serious concern, highlighting the importance of reliable information sources. If you’re looking for a career change to a more stable field, check out some great options like those listed at best online IT courses for career advancement to help you navigate these uncertain times.
Understanding HMPV and its effects is crucial, but a secure future is equally important for your family.
Comparison with Previous Outbreaks
Direct comparison with previous HMPV outbreaks in China requires access to detailed historical data on case numbers, hospitalization rates, and severity of illness. However, anecdotal evidence and reports from healthcare providers suggest that the current surge might be larger or more widespread than previously observed outbreaks. This could be due to the factors already discussed: the effect of reduced immunity following the COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent relaxation of restrictions.
It is important to note that HMPV outbreaks are cyclical, with variations in incidence from year to year, so simply comparing raw case numbers may not provide a complete picture. A more thorough analysis incorporating factors like testing rates, population demographics, and healthcare capacity is necessary for a robust comparison.
Potential Infographic Illustrating the Rise in HMPV Cases
An infographic depicting the rise in HMPV cases over time in China could use a line graph. The x-axis would represent time (e.g., months or years), while the y-axis would show the number of reported HMPV cases. Data points would be plotted for each time period, showing an upward trend during the period following the relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions.
The graph could also incorporate shaded areas representing the periods of strict COVID-19 lockdowns to visually illustrate the correlation between reduced exposure and the subsequent surge in cases. Key data points to include would be the peak number of cases during the current outbreak, the average number of cases in previous years, and the timing of the relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions.
The infographic could also include a small inset map of China showing regional variations in HMPV incidence, if such data is available. This visual representation would effectively communicate the temporal relationship between COVID-19 restrictions and the current HMPV surge.
Prevention and Public Health Measures
Preventing the spread of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) relies on a combination of individual actions and broader public health strategies. Since HMPV spreads similarly to other respiratory viruses, many preventative measures overlap with those used for influenza or the common cold. Effective prevention hinges on both personal hygiene practices and community-wide initiatives.Effective prevention and control of HMPV outbreaks require a multi-pronged approach encompassing individual actions and coordinated public health interventions.
This includes promoting good hygiene practices, implementing vaccination strategies where available, and strengthening surveillance systems to detect and respond to outbreaks effectively.
So, HMPV is hitting kids hard in China right now – it’s a respiratory virus causing a lot of concern. Completely unrelated, but while we’re on health alerts, check this out: Sea and Himalayan salts recalled in Canada: ‘Do not use, serve or’ – definitely something to keep in mind. Back to HMPV, understanding its symptoms is key to managing the outbreak effectively.
Individual Preventative Measures
Practicing good hygiene is crucial in reducing the risk of HMPV infection. This involves frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and water, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching surfaces in public areas. Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick is also vital. If you are feeling unwell, staying home to prevent further transmission is essential. Regularly cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces in your home and workplace can also significantly reduce the viral load.
Consider using hand sanitizers with at least 60% alcohol when soap and water aren’t readily available. Covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets is a simple but effective measure.
Public Health Strategies for HMPV Control
Public health authorities play a critical role in managing HMPV outbreaks. This involves strengthening surveillance systems to track the incidence and spread of the virus. Prompt identification of outbreaks allows for timely implementation of control measures. Public health campaigns can educate the public about preventative measures, promoting hygiene practices and encouraging vaccination where available. Early detection and rapid response are key to minimizing the impact of outbreaks.
Collaborations between healthcare providers, schools, and community organizations are crucial for disseminating information and implementing effective control strategies. Contact tracing, isolation of infected individuals, and quarantine measures may be implemented during outbreaks to limit further transmission.
Examples of Successful Public Health Interventions
Several countries have successfully implemented public health interventions to manage HMPV outbreaks. For example, in some regions, enhanced surveillance systems have allowed for early detection of outbreaks, leading to prompt public health responses. Public awareness campaigns have been effective in promoting hygiene practices and reducing transmission. In some settings, the implementation of infection control measures in healthcare facilities has reduced the spread of HMPV among vulnerable populations.
While there isn’t a specific HMPV vaccine currently available, the success of influenza vaccination programs provides a model for future HMPV vaccine strategies. These interventions highlight the importance of a proactive and multi-faceted approach to managing HMPV outbreaks.
Recommendations for Parents and Caregivers
It is crucial for parents and caregivers to take proactive steps to protect their children from HMPV. Effective strategies are essential for minimizing the risk of infection and mitigating the severity of illness.
- Practice frequent and thorough handwashing.
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals.
- Keep children home from school or daycare when they are sick.
- Ensure children cover their coughs and sneezes.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces regularly.
- Promote good respiratory hygiene practices among children.
- Consult a healthcare provider if your child shows symptoms of HMPV.
Closure
The increase in HMPV cases among children in China highlights the need for heightened awareness and proactive measures. While HMPV shares similarities with other respiratory viruses, understanding its unique characteristics and implementing effective prevention strategies, such as good hygiene and vaccination where available, are key to minimizing its impact. Staying informed and taking preventative steps can significantly reduce the risk of infection and protect vulnerable children.
Top FAQs
Is HMPV contagious?
Yes, HMPV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
How long does HMPV last?
The duration of HMPV illness varies, typically lasting one to two weeks, but severe cases can last longer.
Can adults get HMPV?
While HMPV primarily affects young children, adults can also be infected, though they often experience milder symptoms.
Is there a vaccine for HMPV?
Currently, there isn’t a widely available vaccine for HMPV. Research is ongoing.