Accredited surgical tech programs near me with clinical rotations offer a fantastic pathway to a rewarding career. Finding the right program is crucial, as hands-on experience during clinical rotations is vital for success. This guide will help you navigate the process, from understanding accreditation standards and comparing program curricula to exploring career prospects and applying for admission. We’ll cover everything you need to know to launch your surgical technology career.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the key aspects of finding and enrolling in an accredited surgical technology program. We’ll explore the importance of accreditation, the benefits of clinical rotations, typical program structures, and the career outlook for surgical technologists. We’ll also provide practical advice on the application process, financial aid options, and what to expect during your clinical experience.
Understanding Accreditation for Surgical Tech Programs
Choosing a surgical technology program is a significant decision impacting your career. Ensuring the program’s quality and recognition is crucial, and that’s where accreditation comes in. Accreditation signifies that a program meets established standards of excellence in education and training, preparing graduates for successful careers.
Finding accredited surgical tech programs near you with clinical rotations is key to a successful career. But if the medical field isn’t your thing, consider exploring other options! Check out some top-rated IT courses for beginners with career guidance to see if a tech career might be a better fit. Ultimately, finding the right accredited surgical tech program, or any program for that matter, depends on your interests and career goals.
The Importance of Accreditation in Surgical Technology Programs
Accreditation verifies that a surgical technology program adheres to nationally recognized educational standards. This means the curriculum is comprehensive, covering essential surgical techniques, patient care principles, and safety protocols. Graduates from accredited programs often find it easier to secure employment, as many healthcare facilities prioritize hiring individuals from accredited programs. Furthermore, accreditation may be a prerequisite for certain certifications or licensures, expanding career opportunities.
In essence, accreditation serves as a mark of quality, assuring prospective students and employers that the program provides a high-quality education.
Accrediting Bodies for Surgical Technology Programs
Several organizations accredit surgical technology programs in the United States. Two prominent bodies are the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) and the Accreditation Review Council on Education in Surgical Technology and Surgical Assisting (ARC/STSA). These organizations establish rigorous standards that programs must meet to receive accreditation. The specific requirements can vary slightly between accrediting bodies, but the overall goal is to ensure a consistent level of quality across all accredited programs.
Comparison of Accreditation Standards: CAAHEP and ARC/STSA
Both CAAHEP and ARC/STSA aim to ensure high-quality education in surgical technology. However, their approaches and specific standards may differ slightly. For instance, the detailed requirements for clinical rotations or the specific curriculum components might have minor variations. Both organizations conduct thorough reviews of programs, including on-site visits to assess facilities, faculty qualifications, and student performance. The accreditation process itself is rigorous, demanding continuous improvement and adherence to best practices.
Choosing a program accredited by either CAAHEP or ARC/STSA ensures a strong foundation for a successful career.
Accredited Surgical Technology Programs Near [Location]
The following table lists some example programs. Remember to verify the current accreditation status and contact information directly with the program. This is a sample list and may not be exhaustive.
| Program Name | Location | Accreditation Body | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Program 1 | [City, State] | CAAHEP | [Phone Number], [Email Address], [Website] |
| Example Program 2 | [City, State] | ARC/STSA | [Phone Number], [Email Address], [Website] |
| Example Program 3 | [City, State] | CAAHEP | [Phone Number], [Email Address], [Website] |
| Example Program 4 | [City, State] | ARC/STSA | [Phone Number], [Email Address], [Website] |
Clinical Rotations in Surgical Technology Programs
Clinical rotations are the cornerstone of a surgical technology education. They provide the crucial hands-on experience necessary to translate classroom theory into practical skills and prepare you for the demands of a surgical setting. Without these rotations, your education would be incomplete, leaving you unprepared for the fast-paced and detail-oriented nature of the job.Successful completion of clinical rotations is a requirement for graduation from most accredited surgical technology programs.
These rotations allow you to apply your knowledge, develop your skills, and gain confidence in a real-world surgical environment under the supervision of experienced surgical technologists and surgeons. The experiences gained during these rotations are invaluable and directly contribute to your readiness for employment after graduation.
Types of Clinical Rotations
Accredited surgical technology programs typically offer a diverse range of clinical rotations designed to expose students to various surgical specialties and procedures. This broad exposure is vital for developing adaptability and proficiency across different surgical environments. The specific rotations offered may vary slightly depending on the program and the affiliated hospitals or surgical centers.
- General Surgery: This is a foundational rotation, covering a wide array of procedures, from laparoscopic cholecystectomies (gallbladder removal) to hernia repairs and appendectomies. Students gain experience in preparing the surgical field, assisting the surgeon, and managing surgical instruments and equipment.
- Orthopedics: This rotation focuses on procedures involving the musculoskeletal system, such as joint replacements, fracture repairs, and arthroscopic surgeries. Students learn to handle specialized orthopedic instrumentation and assist in the precise placement of implants.
- Cardiothoracic Surgery: This is a highly specialized area involving procedures on the heart and lungs. Rotations in this area require a high level of precision and teamwork, and students learn to assist in complex procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and valve replacements.
- Neurosurgery: This demanding field involves procedures on the brain and spinal cord. Students learn about sterile techniques in neurosurgery, the use of specialized instruments, and the importance of meticulous precision in this delicate surgical area.
- Urology: This rotation focuses on surgical procedures of the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Students will gain experience with procedures such as nephrectomies (kidney removal) and prostatectomies (prostate removal).
- Gynecology: This rotation involves procedures related to the female reproductive system, including hysterectomies (uterus removal) and laparoscopic procedures.
Benefits of Hands-on Clinical Experience
Hands-on experience during clinical rotations is far more valuable than simply reading about surgical procedures. It allows students to:
- Develop practical skills: Students hone their skills in instrument handling, sterile technique, and surgical preparation.
- Gain confidence: Working alongside experienced professionals builds confidence and allows students to overcome initial anxieties about the surgical environment.
- Improve teamwork skills: Surgical teams rely on effective communication and collaboration, and clinical rotations provide ample opportunity to develop these skills.
- Learn problem-solving: Unexpected situations arise in surgery, and rotations provide a setting to learn how to adapt and problem-solve under pressure.
- Network with professionals: Building relationships with surgeons, surgical technologists, and other healthcare professionals can lead to future job opportunities.
Example Clinical Rotation Schedule
A typical clinical rotation week might involve a mix of observing procedures, assisting in various tasks, and actively participating in specific surgical steps. The exact schedule varies based on the specialty and the hospital’s workflow.
| Day | Morning | Afternoon |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Observe general surgery cases (hernia repair, appendectomy) | Assist in preparing surgical trays and instruments |
| Tuesday | Assist in a laparoscopic cholecystectomy | Shadow a surgical technologist in the sterilization department |
| Wednesday | Observe orthopedic surgery (knee replacement) | Practice instrument identification and organization |
| Thursday | Assist in a minimally invasive procedure (laparoscopy) | Attend a surgical technology skills lab |
| Friday | Assist in wound closure | Review surgical terminology and techniques |
Program Curriculum and Structure
Choosing a surgical technology program requires careful consideration of its curriculum and structure. Understanding the program’s design ensures you’re gaining the necessary skills and knowledge for a successful career. This section compares curricula, identifies essential skills, and Artikels the typical program structure.
Finding accredited surgical tech programs near you with clinical rotations is key to a successful career. It’s a demanding but rewarding field, quite different from the tech world, where you might consider a career change after seeing the full stack developer salary expectations and job outlook. However, surgical technology requires hands-on experience, so focus on those clinical rotations!
Surgical technology programs vary slightly in their specific course offerings, but all accredited programs must meet rigorous standards set by national accrediting bodies. These standards guarantee a consistent level of education and prepare graduates for entry-level positions.
Curriculum Comparison of Two Accredited Programs
To illustrate the variations, let’s compare two hypothetical, yet representative, accredited programs: Program A and Program B. While both cover the core competencies, their approach and emphasis may differ.
- Program A: Focuses heavily on hands-on laboratory experiences throughout the curriculum, integrating theory and practice closely. It might offer a dedicated surgical skills lab with advanced simulation technology. Their elective options might lean towards specialized surgical areas like cardiac or neuro surgery.
- Program B: Emphasizes a strong theoretical foundation in the early semesters, followed by a more concentrated clinical rotation experience in the later semesters. Their electives might offer broader healthcare exposure, including opportunities in medical assisting or operating room management.
The key difference lies in the pacing and integration of theory and practice. Program A prioritizes hands-on learning from the beginning, while Program B builds a solid theoretical base before intensifying clinical experience.
Essential Skills and Knowledge
Successful completion of any accredited surgical technology program equips graduates with a wide range of essential skills and knowledge. These are crucial for safe and effective performance in the operating room.
- Sterile Technique and Aseptic Practices: Maintaining a sterile field is paramount. Students learn meticulous techniques to prevent infection.
- Surgical Instrumentation and Equipment: Understanding the function and proper use of surgical instruments is fundamental. This includes proper handling, sterilization, and maintenance.
- Surgical Procedures and Anatomy: A thorough understanding of various surgical procedures and human anatomy is essential for assisting surgeons effectively.
- Patient Care and Safety: Surgical techs play a vital role in patient care, including monitoring vital signs and assisting with patient positioning.
- Medical Terminology and Documentation: Accurate medical terminology and documentation are necessary for clear communication and record-keeping.
- Teamwork and Communication: Effective communication and collaboration with the surgical team are crucial for a smooth and safe surgical procedure.
Typical Program Length and Structure
Most accredited surgical technology programs are designed to be completed within approximately 18-24 months. This typically involves a combination of didactic (classroom) instruction and clinical rotations.
A common structure includes two academic years, each consisting of two semesters. The first year focuses heavily on didactic instruction, covering anatomy, physiology, microbiology, surgical procedures, and instrumentation. The second year is dominated by clinical rotations in various surgical specialties. The total number of clinical hours usually exceeds 1000, providing ample hands-on experience.
Program Progression Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates a typical student’s progression through a surgical technology program:
[Imagine a flowchart here. It would begin with “Start” and proceed through two boxes representing “Didactic Instruction – Semester 1” and “Didactic Instruction – Semester 2”. These would lead to “Didactic Instruction – Semester 3” and “Didactic Instruction – Semester 4”. From there, arrows would branch to multiple boxes representing various clinical rotations (e.g., “General Surgery Rotation”, “Cardiothoracic Surgery Rotation”, “Orthopedic Surgery Rotation”, etc.).
Finally, an arrow would lead to “Graduation”. The flowchart would clearly show the progression from classroom learning to hands-on clinical experience.]
Career Outlook and Job Prospects for Surgical Technologists: Accredited Surgical Tech Programs Near Me With Clinical Rotations
Becoming a surgical technologist offers a rewarding career path with strong job prospects, particularly in areas with a high concentration of hospitals and surgical centers. This section will explore the job market, salary expectations, career progression, and the importance of ongoing professional development for surgical technologists in [Location]. We will focus on realistic expectations based on current market trends.
Surgical Technologist Job Market in [Location]
The job market for surgical technologists in [Location] is currently [insert data on job market strength – e.g., strong, moderate, competitive, etc. Cite source, e.g., Bureau of Labor Statistics data for [Location] or a reputable local employment agency]. This is largely due to [explain reasons for job market conditions – e.g., growth in the healthcare sector, aging population requiring more surgeries, increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures, etc.].
For example, [insert a specific example, such as a recent hospital expansion or a new surgical center opening in the area, citing a source if possible]. The number of job openings is expected to [insert projected growth rate, if available, and cite the source]. Competition for positions may be influenced by the number of graduates from surgical technology programs in the region.
Salary Range for Surgical Technologists in [Location]
The salary for a surgical technologist in [Location] typically ranges from [insert salary range, citing source, e.g., $45,000 to $65,000 annually]. This range can vary depending on several factors, including experience, education, certifications (e.g., Certified Surgical Technologist (CST)), employer type (hospital, outpatient clinic, etc.), and location within [Location] (e.g., salaries might be higher in urban areas). Entry-level positions generally fall at the lower end of the range, while experienced surgical technologists with advanced certifications can command higher salaries.
For instance, a CST with five years of experience in a major metropolitan hospital in [Location] could potentially earn closer to the higher end of the salary range.
Career Paths for Surgical Technology Graduates
Graduates of surgical technology programs have several career advancement options. Many surgical technologists gain experience and then pursue leadership roles, such as becoming a surgical technologist supervisor or team lead. Others might choose to specialize in a particular surgical area, such as cardiovascular surgery or orthopedics, increasing their expertise and earning potential. Some surgical technologists pursue further education to become surgical assistants or operating room nurses.
Further advancement might involve taking on management responsibilities, such as managing a surgical services department.
Importance of Continuing Education and Professional Development
Continuing education is crucial for surgical technologists to stay current with advancements in surgical techniques, technologies, and best practices. Maintaining certifications, such as the CST credential, requires ongoing professional development activities. Attending workshops, conferences, and taking continuing education courses helps surgical technologists enhance their skills and knowledge, increasing their marketability and earning potential. For example, participation in courses focusing on new minimally invasive surgical techniques or advanced sterilization procedures could significantly boost a surgical technologist’s career prospects.
Staying abreast of evolving regulations and safety protocols is also essential for maintaining professional competence and patient safety.
Finding and Applying to Surgical Tech Programs
Landing your spot in a surgical technology program involves careful planning and a strategic application process. Understanding the requirements, deadlines, and the best ways to present yourself will significantly improve your chances of acceptance. This section Artikels the steps to take to successfully navigate the application process and secure your place in the program.
Application Process and Requirements
Surgical technology program applications typically involve submitting a completed application form, official high school or college transcripts, letters of recommendation, and sometimes a personal essay or statement of purpose. Specific requirements vary between programs and institutions, so carefully review the admission criteria for each program you’re interested in. Deadlines are also crucial; most programs have rolling admissions, meaning applications are reviewed as they are received, so the earlier you apply, the better.
Some programs may have strict deadlines, so missing these could prevent you from being considered. Expect to provide proof of immunization records and possibly undergo a background check as part of the application process. Some programs may also require an entrance exam or interview.
Resources for Finding Accredited Surgical Technology Programs
Locating accredited surgical technology programs is essential to ensure you receive a quality education that prepares you for a successful career. Several resources can help you find these programs.
- The Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP): CAAHEP is the primary accrediting body for surgical technology programs in the United States. Their website provides a searchable database of accredited programs.
- The Accreditation Review Council on Education in Surgical Technology and Surgical Assisting (ARC/STSA): ARC/STSA is another important accrediting agency. Their website offers a similar searchable database.
- Your State’s Board of Allied Health Professionals: Your state’s licensing board for healthcare professionals may maintain a list of accredited programs within your state.
- Online Search Engines: A simple online search using s like “accredited surgical technology programs near me” can yield helpful results, but always verify accreditation through CAAHEP or ARC/STSA.
Preparing a Strong Application
Your application materials are your opportunity to showcase your qualifications and suitability for the program. A well-crafted resume and cover letter are vital components.
Resume Tips, Accredited surgical tech programs near me with clinical rotations
Your resume should highlight relevant experience, skills, and academic achievements. Include volunteer work, shadowing experiences in surgical settings (if any), relevant coursework, and any certifications or licenses you hold. Use action verbs to describe your accomplishments and quantify your achievements whenever possible (e.g., “Assisted in 50+ surgical procedures”). Keep it concise and easy to read.
Cover Letter Tips
Your cover letter should express your interest in the program and explain why you’re a good fit. Mention specific aspects of the program that appeal to you and connect your skills and experiences to the program’s requirements. Demonstrate your understanding of the surgical technology profession and your commitment to pursuing this career path. Proofread carefully for any grammatical errors or typos.
Financial Aid and Scholarship Opportunities
Pursuing a surgical technology education can be costly, but various financial aid and scholarship opportunities are available.
- Federal Student Aid (FAFSA): The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is a crucial first step for accessing federal grants, loans, and work-study programs.
- Institutional Financial Aid: Many colleges and universities offer their own financial aid packages, including scholarships and grants, specifically for their surgical technology programs.
- Private Scholarships: Numerous private organizations and foundations offer scholarships to students pursuing healthcare careers. Research scholarships specifically for surgical technology or allied health professions.
- Professional Organizations: Some professional organizations related to surgical technology may offer scholarships or grants to their members or prospective members.
Illustrative Examples of Clinical Experiences
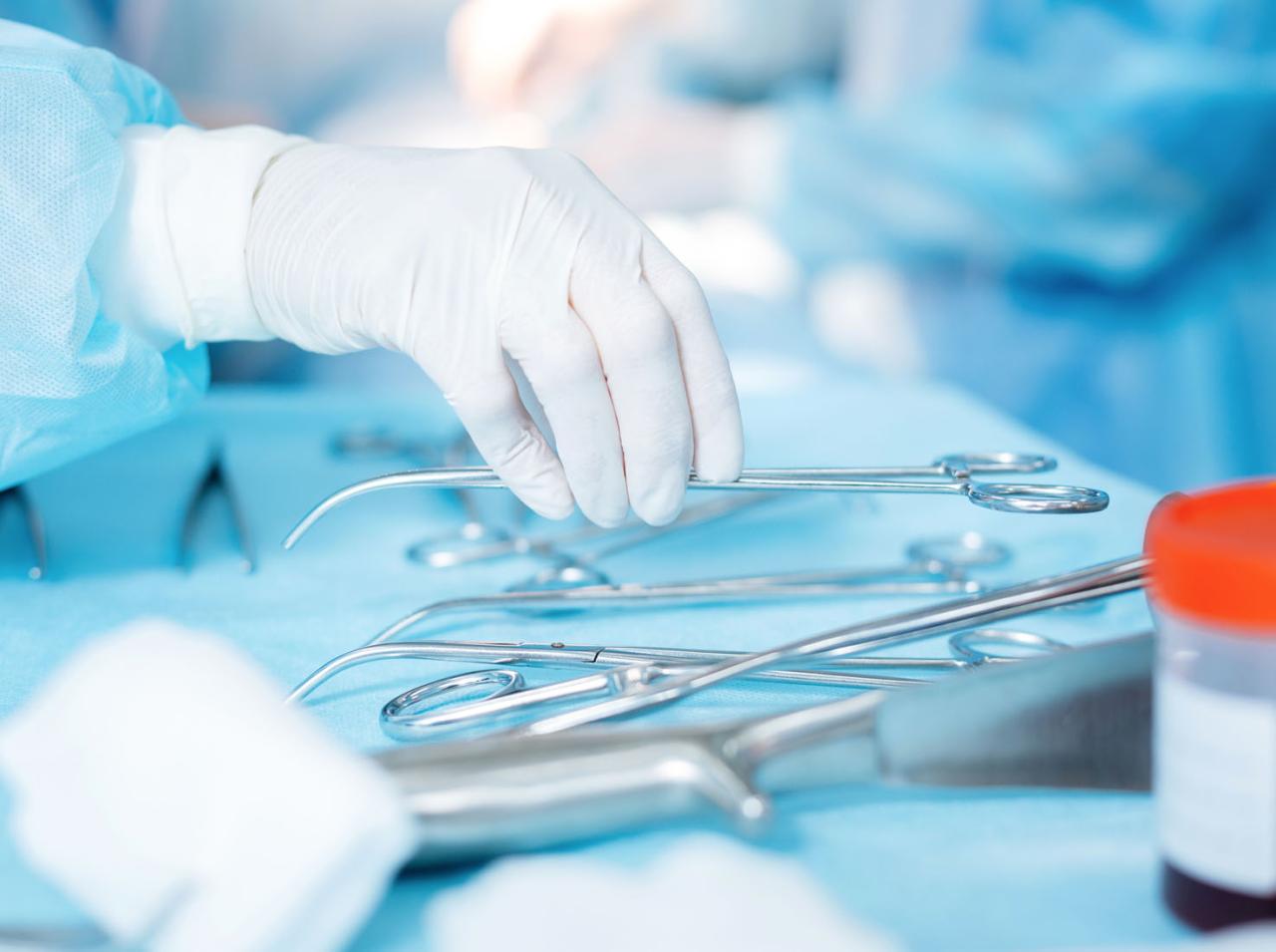
A surgical technologist’s clinical rotation provides invaluable hands-on experience, solidifying classroom learning and preparing them for the demands of the operating room. This section details a typical day, common instruments and equipment, and a potential challenging scenario.
A Typical Day in the Operating Room
A typical day begins with preparing the operating room. This includes checking the sterilization of instruments and equipment, arranging the surgical field according to the surgeon’s preferences, and ensuring all necessary supplies are readily available. The surgical technologist then assists the surgeon and anesthesiologist by prepping the patient, monitoring vital signs, and handing instruments and supplies throughout the procedure.
During the surgery, they maintain a sterile field, anticipate the surgeon’s needs, and assist in wound closure. Post-procedure, they help clean and prepare the operating room for the next case, including properly disposing of sharps and other biohazardous waste. Throughout the entire day, meticulous attention to detail, sterile technique, and teamwork are paramount.
Surgical Instruments and Equipment
Surgical technologists encounter a wide array of instruments and equipment. Basic instruments include scalpels, forceps, retractors, scissors, and needle holders, each with variations designed for specific surgical tasks. More specialized instruments might include laparoscopic instruments for minimally invasive surgery, bone saws and drills for orthopedic procedures, or specialized instruments for neurosurgery or cardiovascular surgery. Equipment utilized includes surgical drapes, suction machines, electrosurgical units (cautery), and various monitoring devices.
Okay, so you’re hunting down accredited surgical tech programs near you with those crucial clinical rotations? That’s awesome! Finding the right program is a big deal, but equally important is figuring out how you’ll present your future career; maybe you’ll need to create a podcast showcasing your skills, which means checking out resources like this guide on finding the right AI voice generator for podcasting to make a professional impression.
Back to those surgical tech programs – good luck with your search!
Understanding the function and proper handling of each instrument and piece of equipment is critical for efficient and safe surgical procedures.
Responding to a Challenging Situation
Imagine a scenario where, during a complex laparoscopic procedure, a crucial instrument malfunctions, causing a delay. The surgical technologist would remain calm and quickly assess the situation. They might immediately notify the surgeon, suggesting alternative instruments or techniques while simultaneously retrieving a replacement instrument from the sterile supply area, maintaining a sterile field throughout the process. Effective communication with the surgical team is crucial, as is the ability to quickly adapt and problem-solve under pressure to minimize disruption to the procedure and ensure patient safety.
The technologist’s quick thinking and preparedness would prevent any significant complications.
End of Discussion
Choosing an accredited surgical tech program with clinical rotations is a significant step towards a fulfilling career. By understanding accreditation standards, comparing programs, and actively engaging in your clinical experiences, you’ll gain the necessary skills and knowledge to excel as a surgical technologist. Remember to thoroughly research programs, prepare a strong application, and seek out financial aid if needed.
Your future in surgical technology awaits!
FAQ Overview
What is the average length of a surgical tech program?
Most programs last around 1-2 years.
How much does a surgical tech program cost?
Costs vary widely, depending on the school and location. Research financial aid options.
What are the admission requirements?
Requirements vary, but generally include a high school diploma or GED and possibly prerequisite courses.
Are there job placement services after graduation?
Many programs offer job placement assistance, but it’s not guaranteed. Networking is key.